by TeachThought Staff
Thinking in the 21 st century is just different.
That doesn’t mean we’re all instantly omnipotent cyborgs, neither do most of us become mindless social media sites addicts that invest our cognitive might touching, swiping, and drooling on our smartphone and tablet computer screens.
But equally as the 19 th century presented one-of-a-kind challenges to information processing contrasted to the 18 th or 20 th, the 21 st century is various from the one prior to it or from the one that will come after.
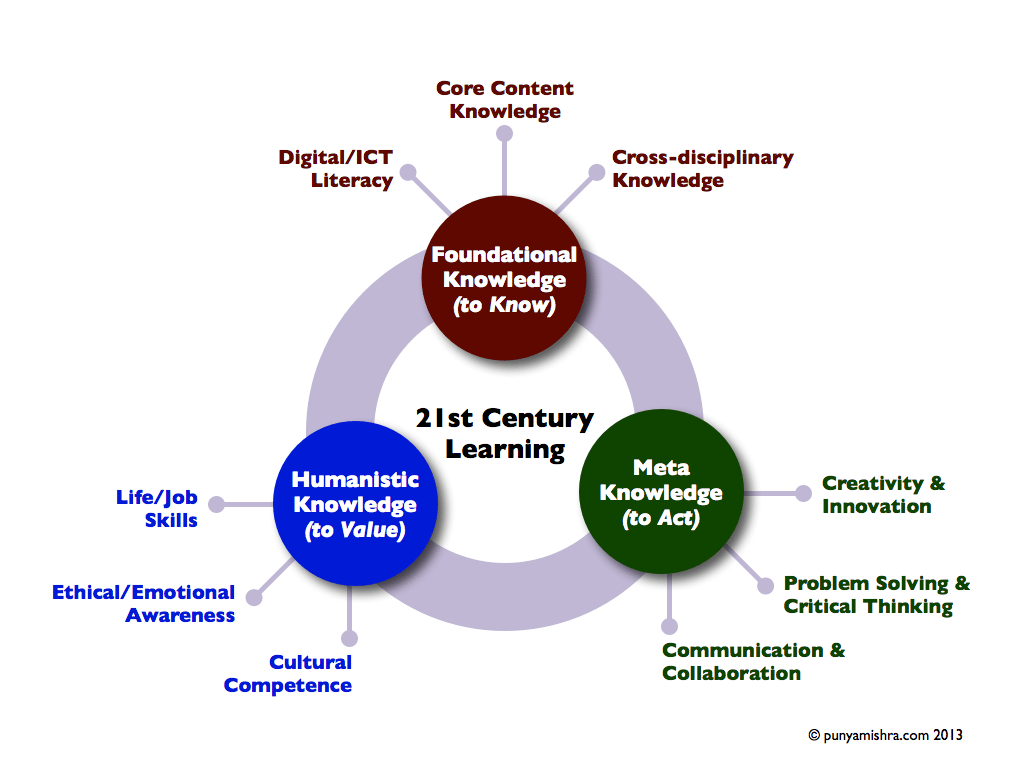
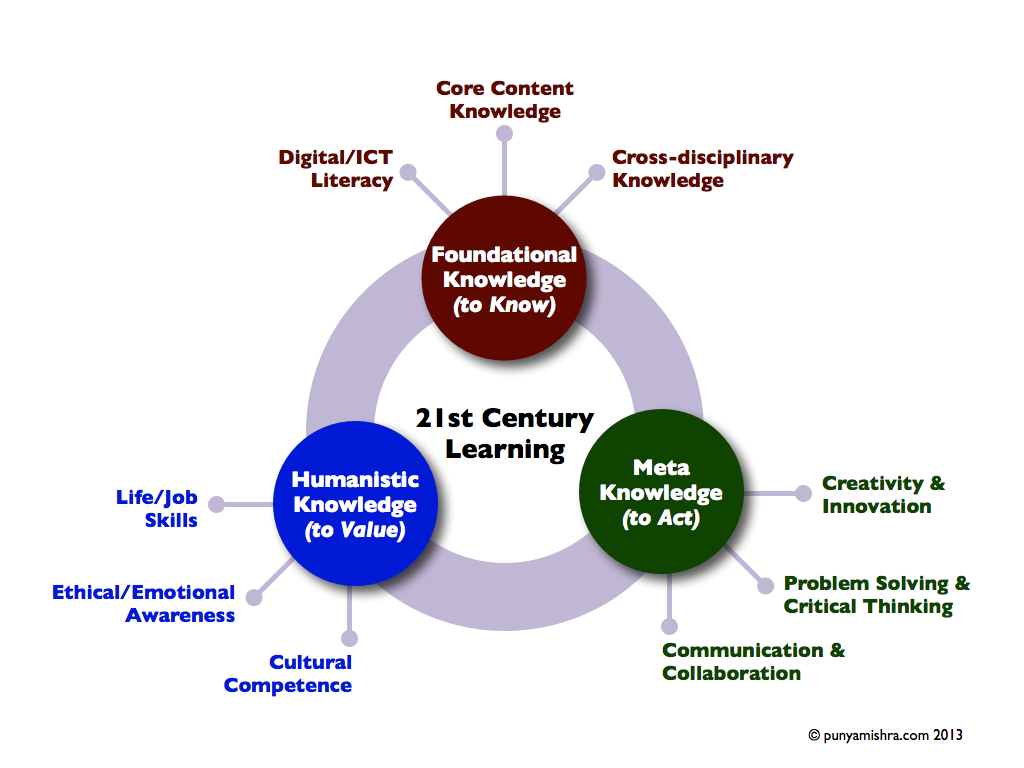
punyamishra.com recently released the adhering to graphic, which I assumed was interesting. It recognized understanding kinds for contemporary discovering, settling on Foundational, Humanistic, and meta understanding.
3 Understanding Domain names For The 21 st Century Pupil
1 Foundational Understanding (To Know)
Digital/ICT Proficiency, Core Web Content Understanding, Cross-disciplinary Understanding
Summary
This domain name includes the basic ideas and concepts that develop the basis of different disciplines. It consists of topics such as maths, lives sciences, background, and language arts. Fundamental understanding offers the framework for comprehending more specialized areas of understanding and is important for crucial reasoning, analytical, and interaction skills.
Examples Of Foundational Expertise
Example 1: In a math classroom, students can learn foundational principles such as addition, reduction, reproduction, and division via hands-on tasks like imagining mathematical operations utilizing manipulatives (such as blocks or counters).
Example 2: Educators can introduce fundamental knowledge of chemistry by carrying out hands-on experiments to explore the homes of various components, compounds, and chain reactions, such as mixing acids and bases to observe changes in pH.
Example 3: Teachers can introduce foundational expertise of globe history by analyzing timelines and maps to map the major events, activities, and empires that have shaped international people in time.
Example 4: Educators can incorporate humanistic understanding by assessing the personalities, motivations, and ethical predicaments offered in literary texts, motivating students to empathize with varied perspectives and experiences.
Example 5: Students can learn more about fundamental ideas in physics by carrying out experiments to comprehend Newton’s laws of motion, making use of basic products like ramps, rounds, and spring scales.
2 Humanistic Knowledge (To Value)
Life/Job Abilities, Ethical/Emotional Understanding, Cultural Skills
Summary
Humanistic understanding focuses on researching human experiences, values, and societies. It includes literature, approach, art, religious beliefs, and ethics disciplines. Humanistic understanding aids people discover concerns of definition, identity, principles, and social justice, fostering empathy, imagination, and a much deeper understanding of the human condition.
Instances Of Humanistic Understanding
Example 1: Pupils can use creative writing workouts to reveal their ideas, feelings, and insights, drawing ideas from compositions and personal experiences to discover motifs of identification, belonging, and self-discovery.
Example 2: Teachers can facilitate thoughtful discussions on ageless inquiries such as the nature of reality, the significance of life, and the existence of free choice, motivating trainees to examine their own ideas and assumptions critically.
Instance 3: Students can engage in disputes and Socratic discussions to discover honest problems and moral thinking, using thoughtful ideas to real-world issues and moral decision-making.
Instance 4: Educators can integrate humanistic understanding by urging pupils to create artwork inspired by appeal, love, struggle, and improvement, using various media and strategies to reveal their concepts and emotions.
3 Meta Knowledge (To Act)
Creativity and Advancement, Problem-Solving and Vital Thinking, Communication and Partnership
Summary
Meta-knowledge describes understanding about understanding itself– the procedures, structures, and approaches associated with acquiring, organizing, and reviewing information. It incorporates crucial believing abilities, information proficiency, research methodologies, and metacognition. Meta understanding encourages people to end up being lifelong students, adapt to transforming atmospheres, and make informed decisions in a rapidly advancing globe.
Examples
Instance 1: In any discipline, educators can incorporate vital assuming abilities by posing flexible questions that call for trainees to examine info, examine proof, and construct reasoned debates supported by proof and reasoning.
Instance 2: Educators can use study or real-world circumstances to challenge pupils to apply important believing skills to intricate problems and decision-making scenarios, urging them to take into consideration several point of views and evaluate the implications of their selections.
Instance 3: Trainees can utilize metacognitive devices such as idea maps, visuals coordinators, or finding out journals to arrange and examine their ideas, connect new info with prior knowledge, and recognize patterns or voids in their understanding.
Utilizing This Design In Your Class
The easiest means to utilize this type of version in your classroom is to consider it a structure for preparation, whether at the device, lesson, or activity level. In that means, you could attempt to have an equilibrium across the 3 understanding domain names, or one system heavily pursuant of Humanistic Expertise (a To Eliminate A Mockingbird novel study, for example), while one more project-based discovering device concentrates on Meta Understanding.
But on a broader and possibly more subjective degree, this visuals can act as a simple suggestion that our work as educators are to aid pupils understand just how to know, value, and act, no matter that the majority of these seem to go beyond typical class assessment tools.
The principle of understanding domain names can sustain the growth of essential thinking skills. Students can learn to examine and evaluate information, identify patterns, and wrap up by engaging with domains (one of many) like foundational expertise. Humanistic knowledge promotes empathy, perspective-taking, and the capacity to take into consideration varied perspectives, while meta-knowledge cultivates metacognition, info proficiency, and the ability to believe reflectively about one’s assuming process.
The huge idea of all learning then might start with understanding, which results in valuing, which informs activity in relevant and authentic neighborhoods.
Owner & & Director of TeachThought